Series Circuits
Imagine the current leaving a battery. If the resistors are connected in such a way that the current must entirely flow through every resistor before returning to the battery, then the circuit is a series circuit.
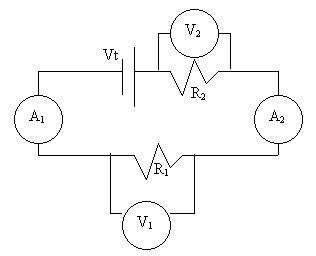
A1 and A2
represent two separate measurements of current intensity at two different
points in the circuit. V1 and V2 represent two separate
measurements of voltage or potential difference. Note how we connect the
voltmeter: one connection at each end of the resistor.†
For series circuits:
Vt = V1 + V2 As the electrons flow through each resistor they lose their potential energy in sequence, in a similar way that skiers gradually lose potential energy on the way down a ski hill. When they take the lift † back up, they are re-energized.
I1 = I2 = constant. The current is constant. The same number of electrons flows through the circuit per second.
If we divide each voltage by the constant current, according to Ohmís Law we will obtain resistance:
Rt = R1 + R2
If there are more resistors in the circuit, then the same rules apply:
Vt = V1 + V2+ V3 + Ö.
I1 = I2 = I3 = constant
Rt = R1 + R2+ R3 + Ö
Example 1
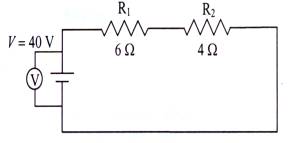
a. What is the total resistance of the circuit?
††††† Rt = R1 + R2
††††† Rt = 6 + 4 = 10 W. (Assuming
that there is negligible resistance in the wires and meters).
b. What current would be measured in between the two resistors?
![]()
![]() The current measured anywhere in the circuit would be the
same.
The current measured anywhere in the circuit would be the
same.
I = Vt/Rt ( Ohmís Law)
I = 40/10 = 4 A.
c. What voltage(V1) would be measured across R1? Across R2?
Using the
fact that current is constant, V1 = I R1 = 4(6) = 24 V.
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† V2
= I R2 = 4(4) = 16 V.
Example 2
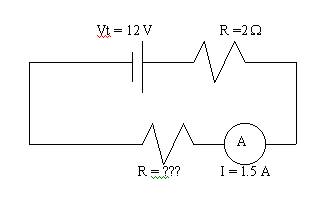
a.†††††††† Find the missing resistance in the circuit shown, which consists of a 12 V battery hooked to two resistors.
The total resistance is Vt/ I =
12/1.5 = 8 W.
R = 8 Ė 2 = 6 W, since
Rt = R1 + R2.
- If the two resistors represented two light bulbs, and one of the light bulbs was off, would you be able to turn the other bulb on?
No. Thatís a disadvantage of a series circuit. The current cannot be interrupted; otherwise, no current flows through other components.
Example 3
†††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††
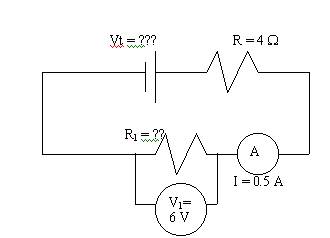 a.†††††††† Find the value of R1 in the
circuit shown.
a.†††††††† Find the value of R1 in the
circuit shown.
Since V1
= I R1, then R1 = V1/I = 6/ 0.5 = 12 W.
b.†† ††††What is the voltage of the battery?
Rt = R1
+ R2 = 12 + 4 = 16
W.
Vt = I Rt = 0.5(16) = 8 V.