Solutions to Exercises
1. An
electric circuit is illustrated below.
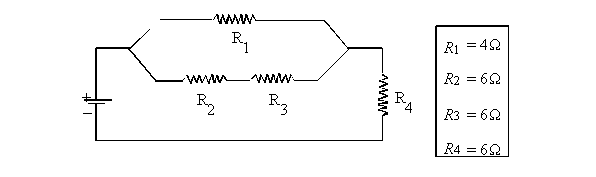
What is the equivalent resistance of
this circuit?
R2 + R3
= Req
6 + 6 = 12 W
1/Rp = 1/R1 +
1/Req
1/Rp = 1/4+ 1/12
Rp = 3 W
Rt = 3 + 6 = 9 W
2. An
electric circuit is illustrated below.

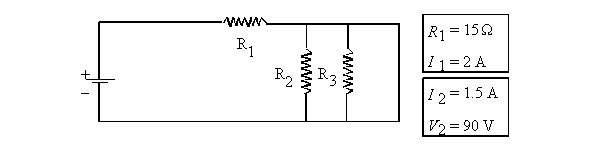
What is the value of resistor R3?
I1 = I2 + I3
because I1 is the total current in this case.
2 = 1.5 + I3
I3 = 0.5 A
If V2 = 90 V, then V3
= 90 V because voltage is constant in parallel.
R3 = V3/I3
= 90/0.5 = 180 W
3. A
series-parallel electric circuit is illustrated below.
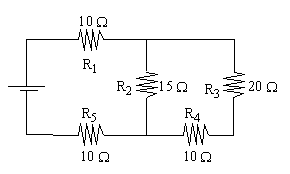
Find Rt.
R4 and R3 are in series so Req1 = R4 + R3 = 10 + 20 = 30W.
R2 and Req1 are in parallel, so
1/ Req2
= 1/ R2+ 1/ Req1
1/ Req2
= 1/ 15+ 1/ 30
Req2
= 10 W.
Rt = R5
+ Req2+ R1 = 10 + 10 + 10 = 30 W.
4. A
series-parallel electric circuit is illustrated below.
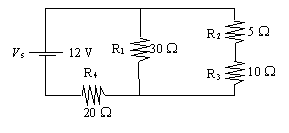
What is the potential difference
across the terminal of resistor R1?
|
|
First find total resistance: 1/Req = 1/R1
+ 1/(R2 + R3) 1/Req = 1/30+ 1/(5
+ 10) |
=
10 W.
Rt = R4
+ Req = 20 + 10 = 30 W.
It = V/R = 12/30 = 0.40 A
V4
= IR4 = 0.40(20) = 8 V
V1
= Vt V4 = 12 8 = 4 V
5. A
series-parallel electric is illustrated below.
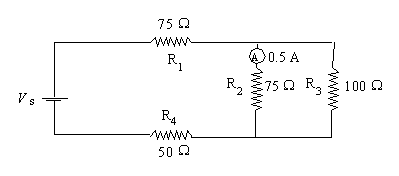
What is the intensity of the current
flowing from the power source, Is?
R2 and R3 experience the same voltage,
so V2 = I2R2 = (0.5)75 = 37.5 V and
I=
V3/R3 = 37.5/100 = 0.375A
So
total current = 0.5 + 0.375 = 0.875 A
6. The following electric circuit consists
of a power supply, five resistors (R1, R2, R3,
R4 and R5) and an ammeter![]() .
.
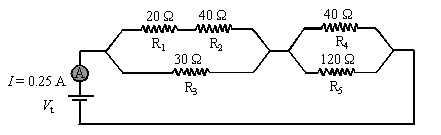
The ammeter reads 0.25 A.
a. What is the potential difference
(voltage), Vt, across the
terminals of the power supply?
1/ Req1
= 1/(R1 + R2) + 1/R3
1/ Req1
= 1/(20 + 40) + 1/30
Req1
= 20 W.
1/ Req2
= 1/R4 + 1/R5
1/ Req2
= 1/40 + 1/120
Req2
= 30 W.
Rt = Req1
+ Req2 = 20
+ 30 = 50 W.
Vt = IRt =
0.25 (50) = 12.5 V
b. What is the potential difference across R3?
Vp =V3 = It Req1
=0.25 (20) = 5V
c. What
is the potential difference across R1?
I1
= Vp/(R1+R2) = 5/(20 + 40)= 0.0833A
V1 = I1R1
= 0.0833(20) = 1.67V
d. What current flows through R5?
V5 = Vt V3 = 12.5 - 5 = 7.5 V
I5
= V5/R5 = 7.5/120 = 0.0625 A
7. An
electric circuit is illustrated below.
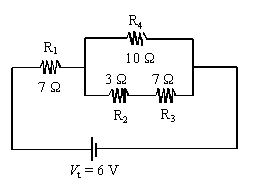
What is the current intensity, I, in resistors R2 and R3?
Req = 1/R4 + 1/(R2+R3)
Req
= 1/10 + 1/( 3 + 7)
Req
= 5 W.
Rt
= R1 + Req = 7 + 5 = 12 W.
It
= Vt/Rt = 6/12 = 0.5 A
The
current flowing through R2 and R3 will be the same as whats on top (since R is the
same), so it will be 0.5/2 = 0.25A
8. The following electric circuit consists
of a power source, five resistors (R1, R2, R3,
R4 and R5) and two ammeters ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
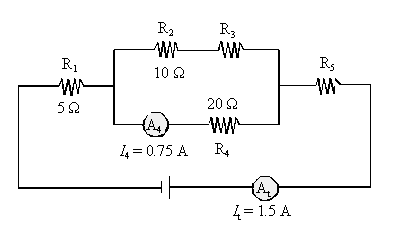
What is the potential difference
(voltage) across the terminals of resistors R3?
R2 and R3 are receiving 1.5 0.75 = 0.75
A.(same current!) That implies that R2 + R3 = R4.
So
R3 = 20 10 = 10
W.
9. The following circuit consists of a
power source, two ammeters ![]() and
and![]() , a voltmeter
, a voltmeter ![]() and three resistors (R1,
R2 and R3).
and three resistors (R1,
R2 and R3).
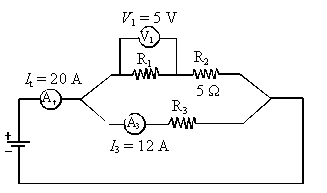
The total current intensity It is 20 A. Current intensity I3 is 12 A. The
potential difference (voltage) V1
across the terminals of resistor R1 is 5 V.
What is the resistance of resistor R3?
I1 = It- I3 = 20 -12 = 8 A = I2
V2
= I2R2 = 8(5) = 40 V.
V1
+ V2 = V3
5
+ 40= V3 = 45 V
R3= V3/I3 = 45/12 = 3.75 W.
10. A source with a potential difference of
30 V is connected to the circuit shown below.
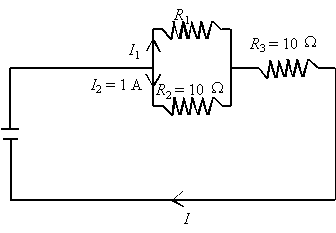
What is the current intensity I across the circuit?
V2 = I2R2 = 1(10) = 10 V
V3
= Vt V2 = 30 10 = 20 V
It
= V3/R3 = 20/10 = 2 A
11. The following electrical
circuit consists of a power source, four resistors (R1, R2,
R3 and R4) and a voltmeter V4 (Vs = Vtotal).
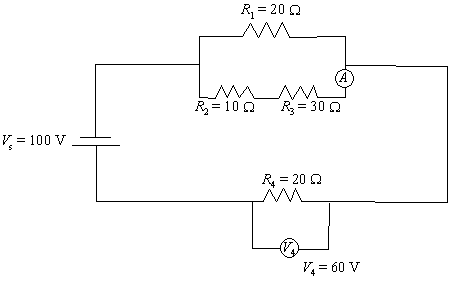
What is the current intensity (I3)
through R3?
V2and3 = 100 60 = 40 V
I3 = V2and3/(R2
+ R3)= 40/(10+30) = 1.0 A
12. How can one 25 W and two 100 W resistors be connected
so that their total resistance is 75 W?
Place the two 100 W resistors in parallel
(so Req = 50 W)and put the new branch in series with the 25 W.
13. How
can four 1.0 W resistors and one 2.0 W resistor be connected
to give a combined resistance of 1.5 W?
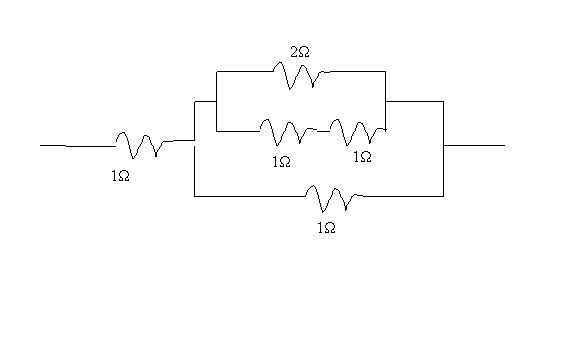
14. Four identical
resistors are connected as shown. If the total voltage is 12V, find the voltage
across each resistor.
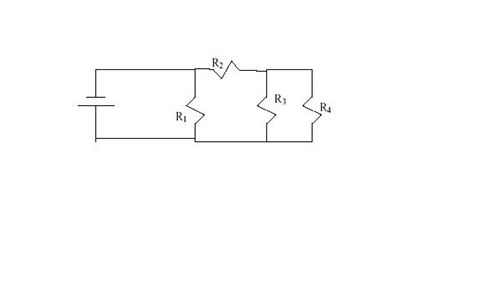
R1 has the full 12V.
Its not in series with anything.
R2 has twice the
resistance of R3 and R4
combined (confused? Just assign any value(for example 1 ohm to all 4 identical resistors, and
work it out), so it will have twice the voltage. 12 = 2x + x; x = 4 V.
Conclusion V2 = 2x = 8V;
V3 and V4 = 4V.