January Review # 6
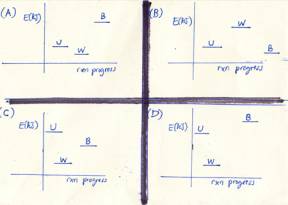 1. Consider
the following:
1. Consider
the following:
U an
uncooked chicken
W a
well-cooked chicken
B a
burnt chicken
Which of the enthalpy versus
reaction-progress diagrams shown to the left is correct?
 2. Suppose
that a certain reaction rate is defined by
2. Suppose
that a certain reaction rate is defined by
R = k [W]3[Q]2
where k = reaction constant
[W] = concentration of gas W in
moles/L
[Q] = concentration of gas Q in
moles/L
A chemist repeated the reaction and found 40 mL of product after 140 s. Originally
it had taken the reaction 70s to produce 40 mL. By what factor did he change the
concentration of W if he had used half as much Q?
3. A
helium balloon is attached to a string. The right mass is tied to the other end
of the string so that the balloon is  suspended in the air: it neither
rises nor sinks. According to the principle of buoyancy, the mass needed to
suspend the balloon is given by:
suspended in the air: it neither
rises nor sinks. According to the principle of buoyancy, the mass needed to
suspend the balloon is given by:
![]() ,
,
where mload
= attached mass + mass of string and balloon’s plastic in grams
VB
= volume of balloon
rair = density of air in g/L
rHe = density of He in g/L
volume of balloon = 10.0 L
temperature = 20.0 oC
pressure = 101.3 kPa
average molar mass of air = 28.9 g/mole
a. Calculate the mass needed to suspend the balloon.
b. Rewrite the formula so that a student can directly plug in V, P, R, T
and the molar masses in order to obtain m.
c. Experimentally, how could you figure out the necessary mass using a
bunch of grapes, a string and a He balloon? (I 've done this a few times when bored at weddings.)
d. BONUS: Derive the formula given in the problem.
4. Using
the table below, find the average at which HI is produced in the last 20
seconds of the reaction. Express your answer in moles/s.
H2 + I2 à 2HI
|
Time (s) |
Remaining Amount of Iodine (moles) |
Amount of iodine that reacted(moles) |
|
0 |
2.6 |
? |
|
10 |
1.9 |
? |
|
20 |
1.4 |
? |
|
30 |
1.2 |
? |
5. Given: O2(g) + H2(g) à 2 OH(g) DH = 77.9 kJ
O2(g) à 2 O(g) DH = 495 kJ
H2(g)
à 2 H(g) DH = 435.9 kJ
Calculate DH for the following reaction: O(g)
+ H(g) à OH(g)
6. At
constant temperature, what happens to the volume of an ideal gas if its
pressure is decreased to one third of its
original value? Also show the result on a graph.
7. In
each case, point out (with a simple yes/no) whether the activation energy will
be raised in the main reaction.
a.
adding
the preservative calcium propionate to bread to slow the growth of mold______
b.
treating a cut with iodine to inhibit the function of
bacterial proteins._____
c.
destroying
enzymes by adding mercury and silver_______
d.
producing
chlorophyll(catalyst) in early spring_____
e.
adding
lactase(an enzyme=catalyst) to milk to break down lactose_______