Phys Sc 416/30
Pretest 1.2 Solutions
1. True? Or False?
a.
Democritus’ model can be used to explain physical changes._TRUE_______
b.
c.
Bohr’s model has electrons moving in orbit-like paths TRUE_______
d.
Excited electrons sometimes emit light after returning to “orbits” that
are closer to the nucleus_ TRUE_______
e.
Electrons are heavier than neutrons_
FALSE_______
2. Explain
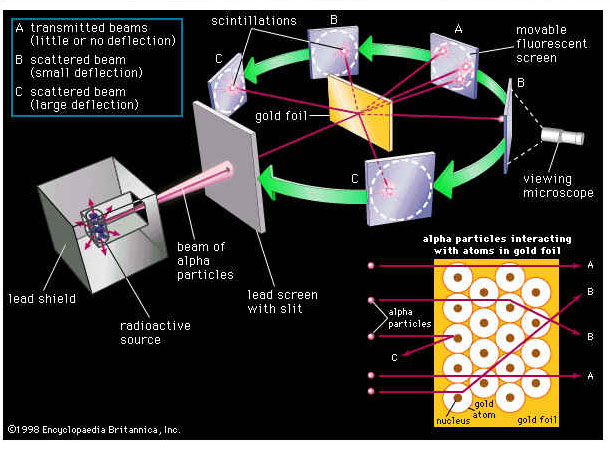
Rutherford and his team beamed alpha particles through gold
foil and detected them as flashes of light or scintillations on a screen. The
gold foil was only 0.00004 centimeter thick. Most of the alpha particles went straight
through the foil, but some were deflected by the foil and hit a spot on a
screen placed off to one side. Geiger and Marsden
found that about
one
in 20,000 alpha particles had been deflected 45o or more.
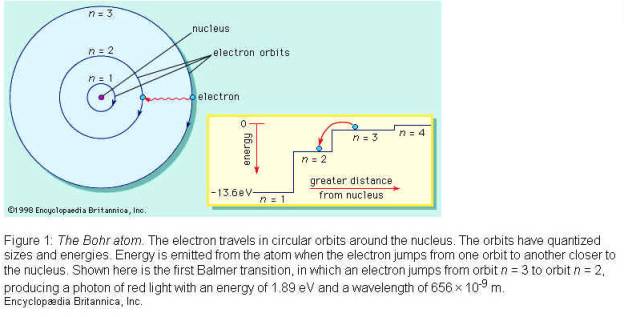
3. How do electron ”orbits” help explain
hydrogen’s spectrum?
Each time
an electron gets excited to a higher energy level it emits a colour of a very specific wavelength because it can only
fall back to one specific energy level. In all there are a very limited number
of energy levels, so only a few coloured lines appear
in an element's spectrum.
4. List two differences between the Bohr
model and the modern model.
|
Bohr |
Modern |
|
No neutrons |
Neutrons exist in nucleus |
|
Energy levels |
Energy levels (shells) with specific number of electrons per
shell |
5. Complete the following table:
|
Name |
Isotope Notation |
Atomic
Number |
Mass
Number |
Number
of Protons |
Number
of Neutrons |
Number
of Electrons |
|
neutral
oxygen |
16O |
8 |
16 |
8 |
16-8
= 8 |
8 - 0 = 8 |
|
sulfide (-2) |
24S |
16 |
16 +8 = 24 |
16 |
8 |
16-(-2) = 18 |
|
Aluminum (+3) |
27Al |
13 |
27 |
13 |
14 |
10 |
|
silver....(+1).................. |
|
47 |
108 |
47 |
61 |
47 - 1 = 46 |
|
Chloride (-1) |
|
17 |
35 |
17 |
18 |
17 - (-1) = 18 |
6. Give the charge for each of the
following subatomic particles:
a.
proton_____+1_
b.
electron____-1__
c.
neutron_____0__
7. Arrange the following in order, from
the lightest(1) to the heaviest(3).
proton___2___
electron__1____
neutron__3_(slightly heavier than the neutron)____
8. A certain atom has two more protons
than electrons. Its charge is _+2___.
9. Will the chemical properties of helium
change if it loses a(n)________?
a.
electron___Yes. Ions and
neutral atoms have different chemical properties_
b.
neutron____No. Isotopes have
the same chemical properties.
c.
proton_____Yes. You would be
creating a different element.
10. If it was possible to remove 3 protons
from a neutral aluminum:27 atom, what
would you end up with? Show the
full isotope notation of the newly created atom.
|
Before |
After |
|
27Al 13 protons 13 electrons 14 neutrons |
10 protons 13 electrons 14 neutrons 24Ne-3 ( no such thing exists in nature, by the
way) |
11. What are isotopes? Give an example.
Isotopes are different versions of the same elements. They have
different mass numbers.
12.
Show through example how an ion differs from
its neutral counterpart.
Mg+2 does not burn; Mg does.
H+1 reacts with base; neutral
hydrogen does not
13. Draw a shell diagram for each of the
following:
a.

![]()
2e) 8e)

b.
![]() 2e)
8e)
2e)
8e)
c.

![]()
2e)5e)
For (c) the valence # (last shell
electrons) is___5_____.
14. Draw a neutron, including its quarks and show how they add up
to the neutron’s charge.
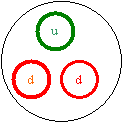
Each d = -1/3
u =2/3
2(-1/3) +2/3 = 0
15. Which particle or form of energy will be emitted when the
radioactive strontium-90 breaks down according to the following?
90Sr à 90Y + __?___
A. alpha B. beta C. gamma D. neutron
90 =90 + x
x = 0 mass
Find atomic numbers:
38 = 39 + y
Y = -1
Answer beta = electron
16. Find
the density of the following liquid:
Mass(g)
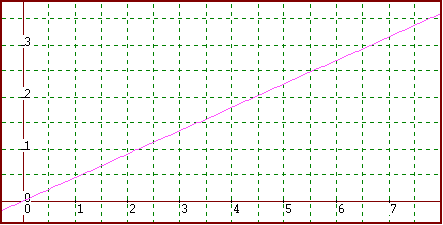
Volume(mL)
density = slope = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1)
= (2.5 - 0) / (5.5 - 0) = 0.45 g/ml
Don't forget that there will be other flashback
questions on characteristic properties, chemical changes, physical changes,
etc!
Sample
Flashback Questions
|
1 |
Which of the following involves a chemical
change?
1.
Boiling water
2.
Putting sugar in coffee
3.
Toasting two slices of bread
4.
Spreading jam on toast
|
A) |
1 |
C) |
3 |
|
B) |
2 |
D) |
4 |
|
2 |
Which of the following is a characteristic
property of mercury (Hg)?
|
A) |
Is has a metallic luster. |
C) |
It is gray. |
|
B) |
It evaporates slowly. |
D) |
Its melting point is -39°C |
|
3 |
A pure gray substance
was placed in a open crucible and heated in the
presence of air. The following
observations were made.
|
|
Before Heating |
After Heating |
|
State |
Liquid |
Solid |
|
Colour |
Gray |
Red |
|
Mass |
12.0 g |
13.2 g |
Which of the following statements IS DEFINITELY
FALSE?
|
A) |
The substance before heating was an element. |
|
B) |
The substance before heating was a compound. |
|
C) |
The substance after heating is an element. |
|
D) |
The substance after heating is a compound. |
|
4 |
While identifying an unknown substance in the
laboratory, you note that it has the following properties:
1. Its melting point is 0°C;
2. It is colourless;
3. It does not change the colour of
neutral litmus paper;
4. It does not conduct electricity.
Which of these properties most clearly
indicates that the unknown substance is pure water?
|
A) |
1 |
|
B) |
2 |
|
C) |
3 |
|
D) |
4 |
Answers
1.C
2.D
3.C ( It's possible for a compound to react with a gas and give a heavier compound, but it is not possible for an element to weigh more than the original substance.
4.A