 Phys Sc 436
Phys Sc 436
Pretest 1.3 with answers
1. Which 3 of the
following elements would you place in the same family, based on their
properties? Justify your choice.
|
Element |
Melting Point(0C) |
Common Ion(s) |
Conducts electricity? |
Appearance |
|
chlorine |
-101 |
-1 |
no |
Yellow-green |
|
barium |
714 |
2 |
yes |
Shiny, silvery |
|
Antimony |
631 |
3,-3,5 |
no |
Dull grey |
|
Copper |
1083 |
2,1 |
yes |
Shiny ,orange |
|
Gold |
961 |
3,1 |
yes |
Shiny, yellow |
|
silver |
1063 |
1 |
yes |
Shiny, silvery |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Copper, gold and silver are all high-melting and shiny. They all
conduct and form the +1 ion.
2. Explain why +1 is the common ion for
alkali metals.
By losing one valence electron, alkali metals become isoelectronic
with noble gases.
3. What noble gas and what charged alkaline earth metal have
the same shell diagram as K+1?
Ar and Ca+2
4. Which of the following is NOT
found in nature?
a. Ar b. Ba c. F-1 d. K+1
Ba ( no full
shell)
5. How can you distinguish between lithium and iron without
weighing or heating them and without reacting them with anything?
Lithium, like all alkali metals, is soft and can be cut with a
knife. Iron can't.
6. What happens when lithium is added to
water?
It reacts to form a base and hydrogen gas.
7. How can you prove that the reaction between calcium and
water generated hydrogen and lime
(an acid –destroying
substance that can be turned into limewater)?
Test for hydrogen:
flaming test will result in a pop.
Blow CO2
into lime + water and it should go cloudy.
8. What is the common ion formed by alkaline earth metals?
+2
9. List three substances that will react with alkaline earth
metals.
Acids, water,
halogens
10. Why are they called alkaline
earth metals?
Alkaline = bases
are formed when water is added to them
Earth = their
bases are poorly soluble in water, like mud
11. Explain why halogens form diatomic molecules. Use dot and
shell diagrams in your explanation.
By sharing one
electron each, both atoms fill their shells.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() F F
F F
![]()
![]()
![]()
12. I am an element that likes to form the -1 ion, and I have the
smallest nucleus among the members of my family. What am I?
F
14. The noble gases don’t burn. Why not?
They are already have the stable
shell diagrams that many other families try to imitate.
15. Which
TWO of the following atomic models represent elements from the halogen family?
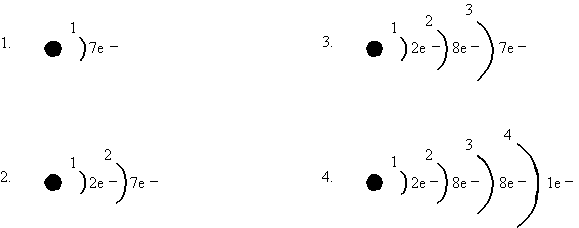
2 and 3. (1
cannot have 7 electrons in the first shell; max = 2)
16. How do you distinguish between a thin plate of silicon from a
plate of silver? List a chemical test and a physical test.
Silicon is not malleable. Silver
is.
Silicon does not tarnish; silver
reacts with pollutants in the air and turns black.
17. With the exception of Se, every other nonmetal can be
distinguished from metalloids by sight alone. How?
All metalloids are grey. With the
exception of Se, all non metals are not grey.
18. Draw appropriate dot structures for the following: Solutions
a. C6H12
b. OF2
c. KI
d. C8(NO2)8 This structure should be the most
symmetric possible. It is the world's most powerful chemical explosive.

Flashback[1]:
19. Which of the following involves a
chemical change?
1. Boiling water______
2. Putting sugar in coffee_____
3. Toasting two slices of
bread____
4. Spreading jam on toast_____
answer: 3
20. Which of the following is a characteristic property of mercury (Hg)?
|
A) |
Is
has a metallic luster. |
C) |
It
is gray. |
|
B) |
It
evaporates slowly. |
D) |
Its
melting point is -39°C |
answer: D