More Pretest 2.2 Type Questions
Combustion and Activation
Energy
1. a. Write
a balanced equation for the combustion of gallium, Ga.
b.
Identify
the fuel, the oxide(s), the agent of combustion and include heat on the
appropriate side of the equation.
c.
Does
the oxide have a higher enthalpy than the oxygen and fuel combined?
Answers
a. 2Ga
+ 1.5 O2 à Ga2O3
+ heat (
Note that gallium is in aluminum’s family, so it acquires a +3 charge. Since
oxygen acquires a –2 charge when reacting with metals, the formula of the
product becomes Ga2O3.
b.
fuel: Ga; agent of combustion: O2; oxide: Ga2O3.
c.
No. Since all combustion reactions are exothermic, the oxides have a
lower enthalpy than the reactants.
2.
For
combustion reactions, is there a difference between kindling point and
activation energy? Explain.
Answer: Of course. The kindling point is the
minimum temperature needed to get a fire going. Activation energy
is the minimum energy needed
to get the fire going. Remember energy and temperature are not the same thing.
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of molecules, and unlike
energy, temperature does not depend on the total mass of molecules present.
3.
If you
wanted to sell kindling wood to help campers start fires in damp conditions,
what kind of kindling point should the wood have? High? Or low?
Answer: low
4.
Complete
the table below for reaction A à B:
Heat of reactants |
50 kJ |
|
Heat of products |
|
|
Heat of
activated complex |
90 kJ |
|
DH |
22 kJ |
|
Ae |
|
Answers:
Heat of reactants
|
50 kJ |
|
Heat of products |
50 + 22 = 72kJ |
|
Heat of activated complex |
90 kJ |
|
DH |
22 kJ |
|
Ae |
90-50 = 40 kJ |
5.
Fill
in the blank: Raising the temperature or adding a catalyst will increase the
number of ___________collisions.
Answer:
effective
6.
If
water does not react with the fuel or, as in the case of oil, if
it does not allow it to float on top of itself, then water
usually puts a fire. Why?
Answer:
Water has a high specific heat so it absorbs a lot of energy and therefore
lowers the temperature of the fuel.
Rate of Combustion
7.
In
each case explain what factor is slowing the rate of combustion.
a.
A
thick tree stands in the middle of a brush fire.
b.
A
small, poorly ventilated room with its windows closed is on fire.
c.
A
campfire at the mercy of elements at the South Pole.
d.
When
asked to gather fuel for the fire, a child throws in a soggy piece of wood.
Answers:
a. low
surface area to weight ratio for the tree
b. lack
of oxygen
c. low
temperature; strong cold wind has cooling effect
d.
Wrong choice of wood (nature of
fuel)
Factors Influencing Rates
8.
Pick
the fastest and slowest reactions from the list below. All are at room
temperature.
a. 2 H3PO4 + 3
Ca(OH)2 à 6H2O + Ca3(PO4)2
b. C4H10 + 6.5 O2 à 5
H2O + 4CO2
c. O2(g) + 2 Cl2(g) à 2
OCl2(g)
Answers: fastest (a): neutralization reaction
Slowest (b): involves
breaking the most and remaking the most covalent bonds
9.
A cube
of calcium is added to water. A second cube is first sliced parallel to one of
its bases and then added to water. Which will react faster, and how much faster
will it react, if all other conditions remain the same?
Answer: The second cube will react faster.
How much faster? Well it it’s sliced in the manner described, we will be
exposing 2 more squares. Picture it. That means that we will have a surface
area of (6s2 + 2s2 ) versus an area of 6s2 for
the unsliced cube of calcium. So the reaction will proceed (6s2 + 2s2
)/ 6s2 = 8/6 =1.33 times faster.
10.
If the
rate of the reaction 2NO(g) + O2(g) à 2NO2 (g) is described by the
formula:
Rate = k[NO]2[O2] where [ ] means concentration, and k
is a fixed number(constant), what will happen if you triple the concentration
of NO gas?
Answer: The reaction will proceed [3]2 times or 9 times faster.
11.
In the
example in which a bacteria attempts to make itself a cell wall, what acts as
an agent which lowers the activation energy, and what raises the activation
energy?
Answer: agent which lowers the activation
energy = catalyst = enzyme.
agent which raises the
activation energy = inhibitor = inhibitor.
12.
Which is the higher temperature? T1? Or T2? Why?
T2
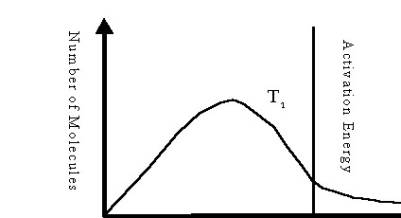
Kinetic
energy (kJ)
Answer: T2 because the area bound
to the right
of the Ae line and under the T2 curve is greater than the area bound to
the right of the Ae
line and under the T1 curve.
13. Given: 2 NO + O2 à 2NO2
Calculate the average rate of NO2 formation for the last 8 recorded minutes.
|
Time (minutes) |
0 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
12 |
|
Amount of O2 disappearing (moles) |
0 |
3 |
4.5 |
5.0 |
5.3 |
5.4. |
5.5 |
Avg. rate of oxygen
disappearance = Dn/Dt = (5.5 -
4.5)/(12-4) = 0.125 moles O2/minute
0.125 moles O2/minute(2 moles NO2/mole O2)= 0.250 moles NO2/min
14. At 20 oC, the following reaction is extremely slow:
CH4 + 2 O2 à CO2 + 2 H2O
Assuming that it takes 50 years for 160 g of CH4 to disappear, at what rate is water produced? Express your answer in ml/year.
(160g CH4/50 years)(mole CH4/16 g)(2 mole water/mole CH4) (18 g water /mole)(1ml/g) = 7.2 ml water /year