Series Circuits
Solutions to p19
1.†††††††† Three 20 W resistors are connected in series across a 120 V generator. What current flows in the circuit?
Rt = 20 + 20 + 20 = 60 W.
Vt = I Rt
120 = I
(60)
I = 2 A.
2.†††††††† Ten Christmas lights have equal resistances. When connected to a 120 V outlet, a current of 0.5 A flows through the bulbs. What is the resistance of just one bulb?
††††††††††† Vt = I Rt
††††††††††† 120 = 0.5 Rt
††††††††††† Rt = 240 W.
††††††††††† Each light bulb will have 240/10 lights = 24 W.
3.†††††††† A lamp with a resistance of 10 W †is connected across a 12 V battery. What resistance must be connected to the lamp to create a current of 0.5 A?
††††††††††† Vt = I Rt
12 = 0.5
Rt
Rt = 24 W.
R + Rlamp = 24
††††††††††† R = 24 -10 = 14 W.
4.†††††††† A 20 W resistor and a 30 W resistor are connected in series and placed across a potential difference of 100 V. Find the voltage drop across each resistor.
††††††††††† Vt = I Rt
††††††††††† 100 = I (20
+ 30)
††††††††††† I = 2 A
††††††††††† V1
= I R1.
††††††††††† = 2(20) =
40 V
††††††††††† V2
= I R2.
††††††††††† = 2(30) = 60 V
5.†††††††† Find the voltage across each resistor, as well as the total voltage.
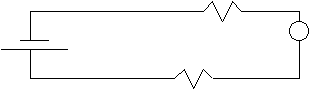 a.
a.
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ††††††††††† 30 W††††††††††††††† A† 0.10 A††††††††
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† †††† 50 W
V1 = 0.10 (30) = 3 V
V2 = 0.10 (50) = 5 V
Vt = 3 + 5 = 8 V
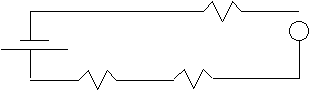
![]() b.
b.
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ††††††††††† 10 W††††††††††††††† A† 0.10 A††††††††
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ††††† 40W
††††††††† ††††††††20 W
V1 = 0.10 (10) = 1 V
V2 = 0.10 (20) = 2 V
V3 = 0.10 (40) = 4 V
Vt = 7 V
6.†††††††† Find the current as well as the voltage across each resistor.
 a.
a.
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ††††††††††† 30 W††††††††††††††† A† ††††††
††††††††††† † 80 V
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† †††† 50 W††††††††††
††††††††††† Vt = I Rt
††††††††††† 80 = I (30
+ 50)
††††††††††† I = 1 A
††††††††††† V1
= 1 (30) = 30 V
V2 = 1 (50) = 50 V
†††††††††††
††††††††††††††††††††††† †††††††††††
 b.
b.
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ††††††††††† 100 W††††††††††††† A† ††††††
††††††††††† † 120 V
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† †††† 150 W††††††††
†††††††††††††††††††††††
Vt = I Rt
††††††††††† 120 = I
(100 + 150)
††††††††††† I = 0.48 A
††††††††††† V1
= 0.48 (100) = 48 V
V2 = 0.48 (150) = 72 V

![]() c.
c.
††††††††††† ††††††† 60V†††††††† ††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† † 100 W††††††††††† A†
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ††††† 80W
††††††††† ††††††††20 W
†††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††
Vt = I Rt
††††††††††† 60 = I (100
+ 20+ 80)
††††††††††† I = 0.30 A
††††††††††† V1
= 0.30 (100) = 30 V
V2 = 0.30 (20) = 6 V
V3 = 0.30 (80) = 24 V
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† †† V=5
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† †† V=5
7.†††††††† 
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ††††††††††† ??? W†††††††††††††† A† 2.0 A††††††††††
††††††††††† † ??? V
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ††† †2 W
†††††††††††††††††††††††
In the above diagram, find the total voltage and the missing resistance.
V2 = I R2 = 2 (2) = 4 V
Vt = 5 + 4 = 9 V
R1 = V1/I = 5/2 = 2.5 W.
8.†††††††† Three known resistances are connected in series
to the terminals of a power source.† The
potential difference at the terminals of the 3.0 W†
resistance is 12 V.
a.†††††††† What
is the potential difference of the power source?
I = 12V/3.0W = 4.0 A
Vt = IRt
= 4.0 (2 + 3 + 4) = 36 V
b.†††††††† What
is the voltage drop across the 4.0 W resistor?
V3 = 4.0(4.0) = 16 V
c.†††††††† What
is the voltage drop across the 2.0 W resistor?
8.0 V
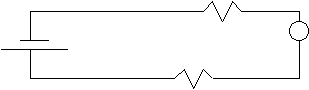 9.†††††††† Use
the diagram to your right, where V1 = 12 V; V2 = 5.0 V.
9.†††††††† Use
the diagram to your right, where V1 = 12 V; V2 = 5.0 V.
a.†††††††† What is the
reading on voltmeter V3?
V1 = Vt = V2 + V3
††††††††††† 12 = 5.0 + V3
††††††††††††††† V3 = 7.0 V
b.†††††††† If the current flowing out of the battery was 125 mA, what would be the value of R2?
125 mA = 0.125 A
V2
= IR2.
5.0 = 0.125 R2.
R2
= 40 W.
![]() 10.†††††† Flashback
10.†††††† Flashback
In an electric circuit, the potential
difference across the terminals of a resistor was set at different levels and
the resulting current intensity was measured.†
The measurements are recorded in the table below.
|
Potential Difference V (V) |
Current Intensity I (A) |
|
0 |
0 |
|
5 |
1.0 |
|
20 |
4.1 |
|
35 |
7.1 |
|
40 |
8.1 |
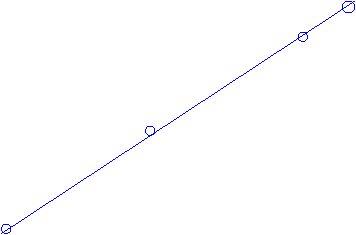
Draw a graph using the above data
and then use the graph to determine the resistance of this resistor.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5††††††††† 10††††††† 15††††††† 20††††††† 25††††††† 30††††††† 35††††††† 40
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† Voltage(V)
Note
although the following seems to involve extra work, it is important to place V
on the x axis because of the ay the experiment was done (thatís why V is in the
first column; it is the independent variable: what we actually controlled in
the experiment)
Slope
= (6-2)/(30-10)= I/V = G =0.20 S
R =
1/G = 1/0.20 = 5.0 W.