Phys Sc 416/36
Series and Parallel: Knowing the Difference
1.
Find
the total resistance and the voltmeter reading at each resistor:
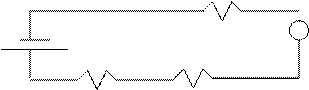
![]() a.
a.
50 W A 0.50 A
40W 30 W
Series circuit RT = R1 +
R2 + R3 = 50 + 30 + 40 = 120 W.
V1= 50(0.5) = 25 V
V2 = 15 V
V3 = 20 V
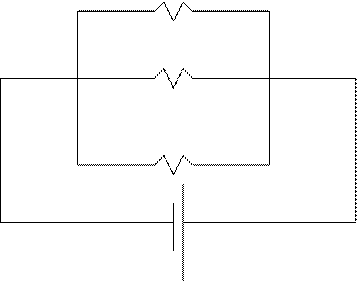 b.
10 W
b.
10 W
10 W
40 W
100
V
Parallel circuit : RT = [R1-1
+ R2-1 + R3-1]-1 = [10-1
+ 10-1 + 40-1]-1 = 4.4 W.
Voltage
is constant, so the voltmeter would read 100 V at each resistor.
The
total current would be IT= V/RT = 100/4.4 = 22.5 A
2.
Two
resistors are connected in parallel. Each draws 2.0 A of current. If the total
voltage is 12 V, find R1 and R2.
R1
= V/I1 = 12/2 = 6 W. Voltage
is constant in parallel.
R2
= V/I2 = 12/2 = 6 W.
3.
Two
resistors are connected in series. The total current is 0.500 A. The potential
difference at the resistors is 2 V and 5V, respectively. Find R1 and
R2.
Current
is constant in series.
R1
= V1/I = 2/0.500 = 4 W.
R2
= V2/I = 5/0.500 = 10 W.
4.
Find
the missing voltage and resistance.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 12V
12V
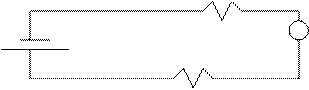
??? W A 3.0 A
??? V
2 W
missing resistor = R1 = V1/I
=12/3 = 4 W.
VT
= I(RT) = 3 (4 + 2) = 18 V.
5. Find the missing voltage.
 10 W
10 W
10 W
![]()
40 W
...............................
????
V
V
= ITRT , but we need RT.
RT
= [R1-1 + R2-1 + R3-1]-1
= [10-1 + 10-1 + 40-1]-1 = 4.4 W.
V
= 2(4.4) = 8.8 V.
6. Find the missing resistance
, the total current, and the missing voltage
![]()
 10 W 1.0
A
10 W 1.0
A
![]()
2.0
A
????
![]()
![]() 40 W 0.25 A ??????
40 W 0.25 A ??????
????
V
V
= I1R1 or I3R3 =1(10) or 0.25(40) = 10 V
IT
= I1 + I2 + I3 = 1.0 + 2.0 + 0.25 = 3.25 A
7. a. In a series circuit, what measurement
is constant at each resistor? Answer: current
b. In
a parallel circuit, what measurement is constant at each resistor? Answer: voltage.