d. 3244 K – 273 = 2971 C > 2970: vibrational, rotational and translational energy.
2. 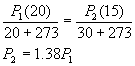
3. mass of H2 = 40.15 – 40.00 = 0.15 kg = 150 g = 75 moles
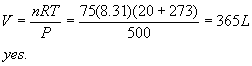
4. Target equation: 2 FeO + 0.5 O2 à Fe2O3
2FeO à 2Fe + 1 O2 DH = + 266.5 (2) kJ
2 Fe + 1.5 O2 à Fe2O3 DH = - 822.2 kJ
2 FeO + 0.5 O2 à Fe2O3 DH = - 289.2 kJ
5. total volume = 200 + 300 ml = 500 ml = 500 g, since they are dilute aqueous solutions.
Q = mcDT
= 500(4.19)(35-20) = 31425 J
But this amount is released by the neutralization reaction so DH= -31.425 kJ
Moles of LiOH = 0.200L X 0.1 mol/L = 0.02 moles
DH= -31.425 kJ/0.02 moles = -1571 kJ/mole of LiOH
6. increase the temperature; powder the Mg to increase the surface area.
7. 1 mg = 0.001g = 0.001/32 = 0.00003125 moles of O2 per second
But ratio of O2 to FeO is 0.5 to 1 or 1 to 2, so 0.0000625moles of FeO are produced in 1 second.
In 60 sec, 60 X 0.0000625 = 0.00375 moles/minute
8. a. BHT and SO2 are both attacked by oxygen. This molecular sacrifice spares our Bordeaux and Cheerios.
b. Chlorophyll indirectly catalyzes the breakdown of water into hydrogen ions and molecular oxygen.
CFC’s release Cl which attacks O3 to form ClO, which in turn reacts to give back Cl.