 | |
|
|
Exercise 3.1
Intro. to Equilibrium
1.Classify as one of the following:
(1)The Irreversible Reaction
(2)Steady State
(3)Reversible Reactions: Equilibrium
a.water in an open dish left to evaporate
b.20 ml of alcohol in a sealed 500 ml jar
c.water flowing into a pool at a rate of 2 L/s and leaving the pool at that rate.
d.adding Mg to acid
e.a saturated salt solution in a closed vessel
2.a. Sugar is added to a cup of coffee until no more sugar can dissolve. The top is sealed so that no coffee can evaporate, and the temperature is kept constant. Hey, we have equilibrium! Agree?
b.Macroscopically, what would you see?
c.Microscopically what is still going on?
3.By burning a log, do you establish equilibrium eventually? Explain.
4.One drop of water placed in a closed bottle may or may not establish a state of equilibrium between gas and liquid according to :
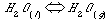
Explain. What will affect whether equilibrium is established?
5.Given:
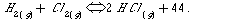
Which information can you obtain from the above chemical equation?
a.the ratio with which hydrogen and chlorine react ?
b.the concentrations of the gases at equilibrium ?
c.whether it is an equilibrium reaction?
d.how fast equilibrium is reached?
e.the physical state of the products and reactants?
f.whether the reaction is exothermic?
g.the reaction mechanism?
6.Give 1 everyday example for each of the following:
(1)The Irreversible Reaction
(2)Steady State
(3)Reversible Reactions: Equilibrium
Copyright ©2001
Created:April/6/1996; Updated:Jan/24/2001